Hepatorenal syndrome in patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis
Peter Jarčuška Orcid.org 1, Ľuboslav Beňa Orcid.org 2, A. Timková Orcid.org 3, Eduard Veseliny Orcid.org 1, Martin Janičko Orcid.org 1
+ Affiliation
Summary
Hepatorenal syndrome is functional kidney failure in patients with portal hypertension and ascites.
Patients: 20 patients (13 men, 7 women) with acute alcoholic hepatitis and hepatorenal syndrome type 1 were hospitalised at the Intensive Care Unit, 1st Dept. of Internal Medicine, University Hospital in Košice. All patients were treated with continual terlipressin infusion (1 mg daily, in case of low effect, dose increased to 2 mg daily) combined with albumin, mean treatment duration was 20.00 ± 11.69 days. Haemodialysis was indicated in 11 patients due to oligo-anuria with hyperhydratation, metabolic acidosis or hyperkalemia.
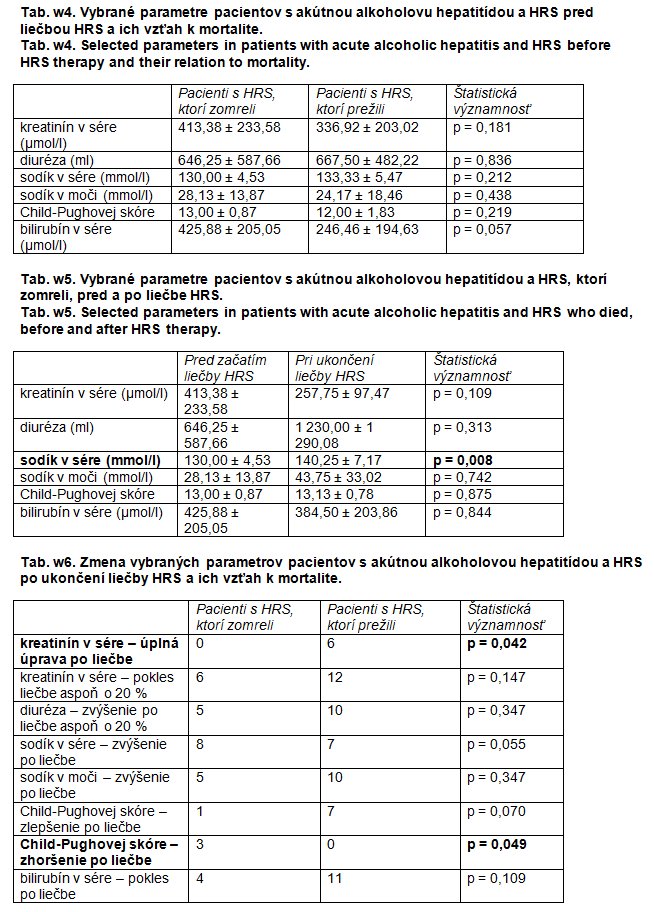
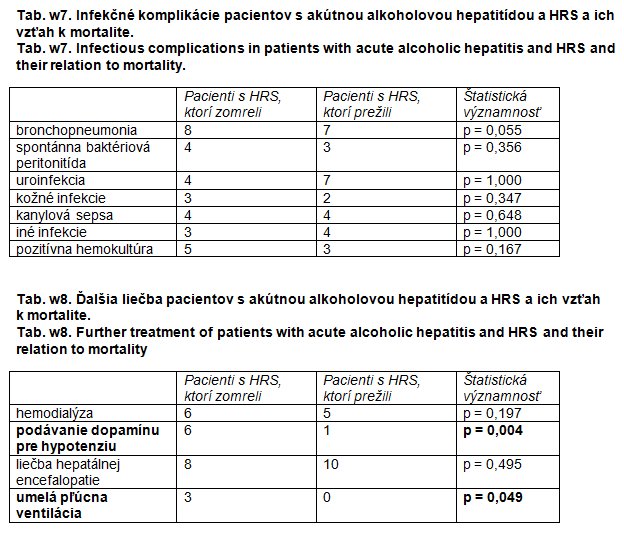
Results: A complete response to therapy (creatinine < 133 μmol/1) was seen in 6 patients (30%), a response to treatment (> 20% creatinine decrease) was observed in 18 patients (90%). Therapy led to an increase in natrium, diuresis and natriuresis and a decrease in serum creatinine and the Child-Pugh score. Hospital mortality was 40%. No pre-treatment parameter except for the grade of hepatic encephalopathy (serum creatinine, bilirubin and natrium, natriuresis, diuresis and Child-Pugh score) was associated with mortality, but patients who survived showed an improvement in liver functions after therapy (Child-Pugh score and bilirubin decrease).
Conclusion: Combined treatment with terlipressin and albumin improves renal functions in patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis and hepatorenal syndrome typel, however, the survival of patients depends on an improvement in liver functions during the treatment.
Keywords
mortality, terlipressin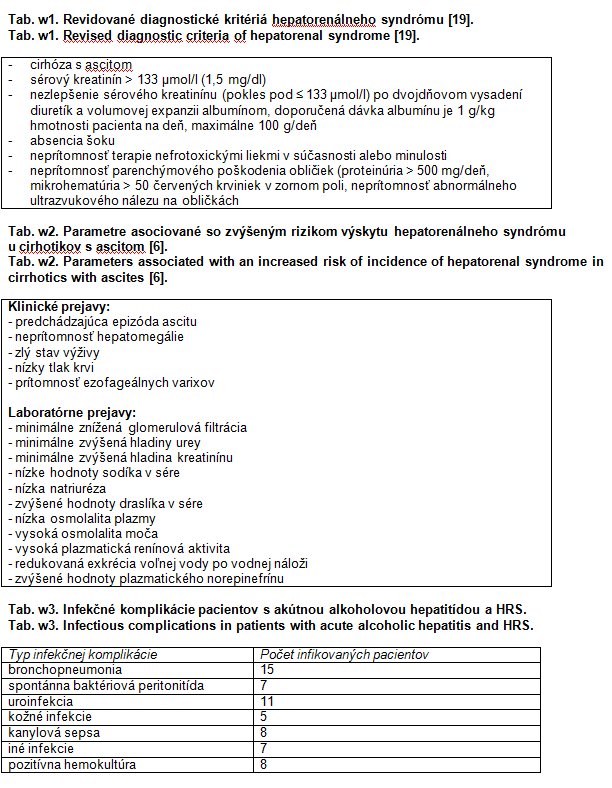
To read this article in full, please register for free on this website.
Benefits for subscribers
Benefits for logged users